Staying ahead in the constantly changing workplace is crucial. Our comprehensive report on key 2025 trends provides valuable insights to help you navigate this dynamic environment. We've analyzed findings from top human resources, work, and labor experts, including those from Harvard Business Review, SHRM, and McKinsey. Using this report, you'll be better prepared to adapt and succeed in the ever-changing workplace.
1. Human-Centric Leadership
The future of leadership is undergoing a profound transformation. By 2025, successful leaders will be distinguished by their ability to empathize, build authentic relationships, and create a sense of purpose within their teams. Employees are increasingly seeking leaders who understand their individual needs, foster a sense of belonging, and actively support their well-being. This shift towards a more human-centric leadership style is driven by changing employee expectations and workplace dynamics.
- The evolving role of AI: As artificial intelligence takes on more routine tasks, human skills like empathy, critical thinking, and emotional intelligence become even more crucial for effective leadership.
- Increased focus on employee well-being: The pandemic highlighted the importance of mental health and work-life balance, prompting employees to seek workplaces that prioritize their overall well-being.
- The need for greater inclusivity: Organizations recognize the value of diverse perspectives and inclusive leadership in fostering innovation and creating a sense of belonging for all employees.
Further amplifying the need for human-centric leadership is the rise of the "quit and stay" trend. With a more stable job market in 2025, employees are less likely to leave their current positions, even if they are dissatisfied. This can lead to a situation where employees remain in their jobs but become disengaged, potentially impacting productivity and morale. Organizations must prioritize employee engagement and satisfaction to combat this, fostering a workplace culture where employees feel valued and supported.
Employee resource groups (ERGs) are also playing an increasingly important role in fostering inclusivity and diversity in the workplace. Tania Holt, a senior partner at McKinsey, emphasizes the urgent need to expand and diversify the current talent pool from which companies recruit. The existing pool is too limited and notably lacks representation of individuals over 55 and women in Europe. These groups provide a platform for employees with shared interests or backgrounds to connect, support each other, and contribute to a more inclusive work environment. By encouraging and supporting ERGs, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to diversity and inclusion, creating a sense of belonging for all employees.
2. AI Integration of HR Practices
Artificial intelligence rapidly transforms HR processes, from recruitment and onboarding to employee engagement and performance management. AI-powered tools can automate time-consuming tasks, reduce bias in hiring, and provide personalized insights for employee development. One key insight is that AI can free HR professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives by automating routine tasks. This allows HR teams to dedicate more time to activities like talent development, employee engagement, and building a positive workplace culture.
However, organizations must approach AI implementation strategically:
- Address employee concerns: Alleviate fears of job displacement by emphasizing AI's role in augmenting human capabilities, not replacing them.
- Ensure data quality: AI's effectiveness relies on accurate and unbiased data. Invest in data management and ensure that AI systems are trained on reliable information.
- Prioritize ethical considerations: The growing significance of AI in boosting productivity and shaping key decisions across industries and job functions has raised ethical concerns among professionals globally. Clear guidelines for responsible AI usage are essential to ensure fairness and transparency to prevent unintended consequences.
- Mitigate potential bias in performance management: While AI can be a valuable tool in performance management, organizations must be mindful of the potential for bias in AI-powered evaluation tools. It's crucial to ensure that these tools are designed and implemented in a way that promotes fairness and avoids perpetuating existing biases.
“Can smart machines outthink us, or are certain elements of human judgment indispensable in deciding some of the most important things in life?” — Michael Sandel, political philosopher; Anne T.; and Robert M. Bass, professor of government.
3. Skills-Based Hiring
With the increasing need for specialized skills, companies are shifting from traditional credential-based hiring to a skills-first approach. This transition is fueled by the widening skills gap caused by rapid technological advancements and evolving job roles, which often demand skills not reflected in traditional resumes. Additionally, skills-based hiring fosters greater agility, enabling organizations to swiftly identify and recruit talent with the precise capabilities needed to adapt to changing business needs. Furthermore, by prioritizing skills over credentials, organizations can cultivate a more inclusive workplace and access a broader talent pool.
Skills-based hiring has a tangible impact on both employees and employers. Research indicates that non-degreed workers hired into previously unavailable roles through skills-based approaches experienced a 25% wage increase and demonstrated greater loyalty to their employers11. Companies that adopt skills-based hiring report a reduction in mis-hires and improved employee performance.
4. Closing the Expertise Gap
Organizations are facing an expertise gap as a large portion of the workforce nears retirement, and technological disruptions reshape job roles. This trend will continue into 2025, according to reports from McKinsey. In a mid-point scenario, 400 million workers will be affected by automation or, more broadly, technology, along with 300 million "more" people aged 65 and older than there were in 2014.
These gaps present a rapid and significant challenge for organizations as they strive to retain and transfer knowledge from experienced workers while adapting to new technologies and skill requirements. Businesses should focus on implementing robust knowledge management systems, developing clear succession plans, and investing in upskilling programs to navigate this challenge successfully. These strategies will facilitate the seamless transfer of knowledge and skills, ensuring that organizations remain agile and competitive amidst shifts in the job market.
5. Improving Employee Benefits
Employee benefits are no longer just about healthcare and retirement plans. In 2025, organizations are offering a wider range of benefits to meet the diverse needs of their workforce, including:
Mental health support
The American Psychological Association reports that 77% of employees have recently experienced work-related stress. As a result, organizations are expected to proactively incorporate mental health support into their cultures. Leaders can expect to receive training to cultivate inclusive and psychologically safe environments that address both individual and team well-being. Additionally, hybrid work models require clear guidelines and “digital detox” strategies to mitigate burnout. Preventative measures, such as stress audits and resilience training, may become commonplace to reduce absenteeism and promote productivity.
Data-driven insights and AI-powered tools will likely personalize support and enable companies to continuously refine their mental health initiatives. Importantly, organizations may begin to recognize the interconnectedness of mental health and DEI, working to ensure systemic inclusivity for all employees.
SMEs winning big corp on childcare assistance
Emerging as the top trend for work in 2022, the rising cost of childcare has led companies to introduce sophisticated childcare benefits to attract talent. However, many large companies are now cutting back on these offerings, while small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are taking the lead, according to the Best Place for Working Parents National Trends Report. This shift may influence how working parents increasingly turn to the SME segment.
Loneliness and employee well-being
Loneliness is emerging as a significant business risk, affecting employee performance, engagement, and overall well-being. Organizations must recognize the impact of loneliness on their workforce and implement strategies to foster connection and support among employees. This can include initiatives like team-building activities, social events, and mentorship programs, as well as creating a workplace culture that encourages open communication and social interaction.
6. Pay Equity and Transparency
In recent years, pay equity and transparency have become focal points for both regulators and employees. In the United States, over a dozen states, including California, Colorado, and New York, along with Washington, D.C., have enacted pay transparency laws, with several more jurisdictions considering similar measures. These laws often require employers to disclose salary ranges in job postings and prohibit retaliation against employees who discuss compensation. In the United Kingdom, data from the Office for National Statistics indicates that the gender pay gap among full-time employees was 7.0% in April 2024, down from 7.5% in April 2023. To address these disparities, HR teams are encouraged to conduct regular pay audits, benchmark salaries against industry standards, and communicate transparently about pay structures and equity initiatives.
Another key insight from research conducted by Bussines.com is that companies with internal salary transparency have the lowest rates of employees planning to find new roles in the next 12 months. This suggests that pay transparency can be a valuable tool in retaining employees and reducing turnover costs.
7. Hybrid Work Models
The rise of hybrid work models, which blend remote and in-office work, has been fueled by organizations adapting to a geographically dispersed workforce and employees wanting more flexibility. This trend reflects a need to find a middle ground between the flexibility of remote work and the benefits of in-person collaboration.
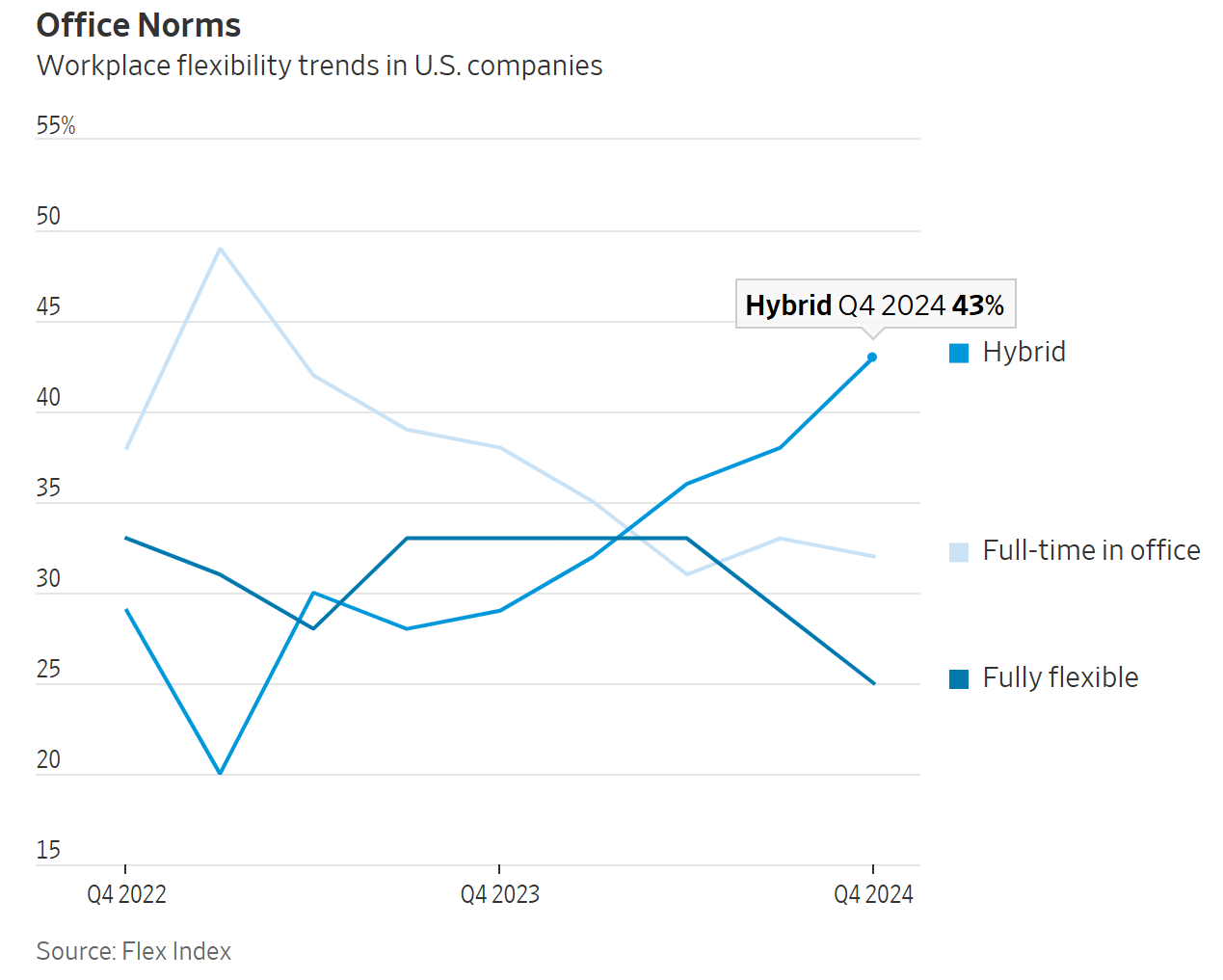
Successful hybrid work models require:
- Clear communication and expectations: Establish clear guidelines for remote work, including communication protocols, performance expectations, and availability.
- Investment in technology: Remote work relies on robust technology infrastructure, including secure remote access solutions, collaboration tools, and video conferencing platforms.
- Focus on employee well-being: Organizations must prioritize employee well-being in hybrid work models, offering flexible schedules, mental health resources, and support for work-life balance.
- Shift from "days in the office" to "core hours" and "focus time": Transitioning from enforcing specific in-office days to implementing core collaboration hours and empowering employees to manage their focused work time independently. This strategy fosters a better work-life balance and autonomy while maintaining efficient teamwork and communication.
While hybrid work offers many benefits, it's important to acknowledge potential downsides. Research suggests that remote work can lead to fragmentation and isolation, potentially impacting employee well-being and team cohesion. Organizations must proactively address these challenges by fostering communication, encouraging social interaction, and creating opportunities for team building in hybrid work environments.
8. The Green Transition
The escalating threat of climate change has extended its impact beyond the environment, permeating the global job market. Despite recent geopolitical setbacks, the inevitable shift towards greener practices, crucial for human survival, is driving this transformation.
Consequently, new employment opportunities are emerging in sectors such as renewable energy, sustainability, and environmental conservation. These roles necessitate a distinct skill set encompassing technical proficiency, analytical thinking, and problem-solving capabilities. In order to keep up with this trend, companies need to put money into training and development programs that will give their employees the skills they need for these new green jobs.
9. Neuroinclusion in the Workplace
Organizations increasingly recognize the advantages of neurodiversity in the workplace, as neurodivergent individuals often bring unique perspectives and skills that can drive innovation and enhance problem-solving. For instance, JPMorgan Chase created an Autism at Work initiative and found that their neurodiverse hires were, on average, 90% to 140% more productive than employees who had been at the company for five or 10 years.
Neuroinclusion involves creating a work environment that is supportive and accommodating to the needs of neurodivergent individuals, such as those with autism, ADHD, or dyslexia. This includes implementing flexible work arrangements, providing clear and structured communication, and fostering a culture of understanding and acceptance. Such practices not only enhance the well-being and productivity of neurodivergent employees but also contribute to a more diverse workforce. By embracing neurodiversity, organizations can tap into a wider talent pool, gain unique perspectives, and foster a more inclusive and creative workplace culture.

Conclusion
The workplace of 2025 is undergoing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements, evolving employee expectations, and broader societal changes. The trends outlined in this report are interconnected and reinforce each other, creating a holistic picture of the evolving workplace. Globalization, demographic shifts, and climate change further influence these trends, demanding that organizations adapt to remain competitive and thrive in this dynamic environment.
By proactively addressing these trends, organizations can create a workplace that is productive, supportive, and fulfilling for all employees. Success in navigating these interconnected trends and their impact on the future of work demands a comprehensive strategy. Organizations need to embrace adaptability, innovation, and employee-centric practices to flourish in the ever-changing landscape of 2025.