The talent acquisition process steps refer to the structured sequence of activities an organization undertakes to identify, attract, assess, hire, and onboard new employees, aligning with strategic workforce goals. While seemingly straightforward, executing these steps effectively requires a deliberate, coordinated approach. Implementing structured, data-driven practices can significantly improve recruitment efficiency; studies and company examples demonstrate potential for substantial reductions in hiring timelines when workflows are optimized. This guide provides a blueprint for the core stages, transforming your process from a reactive filling of seats to a strategic talent acquisition approach. Understanding these steps is foundational to building a robust talent acquisition strategy.
Why Map Your Talent Acquisition Process Steps?
Clearly defining and mapping your talent acquisition process steps delivers significant business advantages. It moves recruitment from an often ad-hoc function to a standardized, measurable operation. This standardization directly impacts cost efficiency by identifying and eliminating redundant activities or ineffective sourcing channels. Mapping reveals bottlenecks, allowing for targeted improvements that accelerate hiring speed, which is critical in competitive talent markets where top candidates have multiple options. Perhaps most importantly, a well-defined process supports a higher quality of hire (QoH). By ensuring consistency in evaluation, aligning steps with required competencies (often informed by skills-first hiring principles and Talent Intelligence, or TI), and fostering positive candidate interactions, a mapped process helps secure talent that not only fills the role but also thrives in the long term.
The 7 Core Talent Acquisition Process Steps
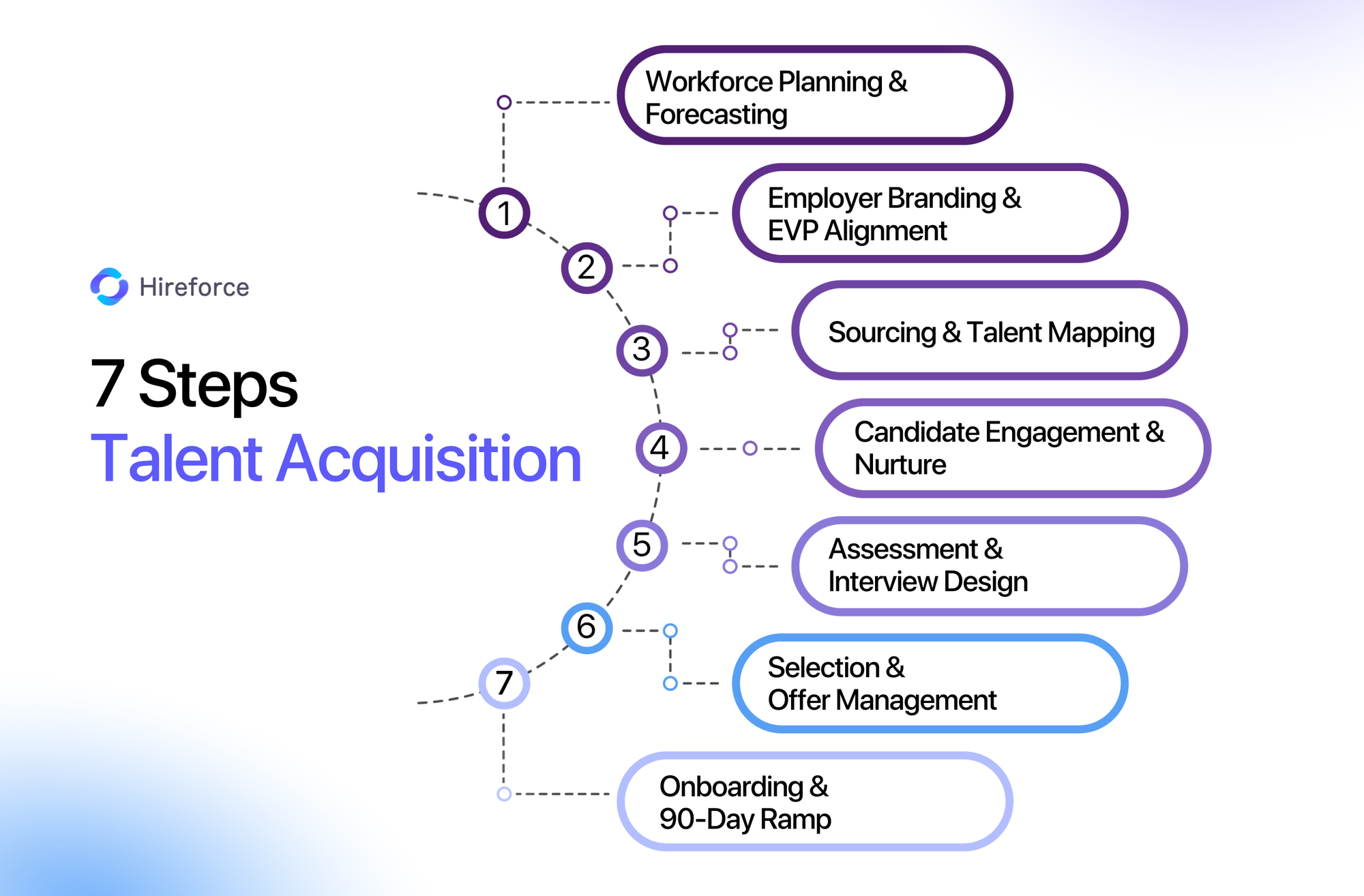
1. Workforce Planning & Forecasting
Before any job is posted, strategic planning must occur. This initial step involves analyzing business objectives to forecast future talent needs (demand) and assessing the current internal skills landscape and external labor market availability (supply). Key activities include rigorous demand vs. supply analysis, identifying critical skills gaps, and developing data-informed headcount plans. The primary output is a clear requisition plan based on prioritized needs. Neglecting this stage results in reactive hiring that is disconnected from long-term goals. A key KPI reflecting success here is the open-requisition fill rate against the plan.
2. Employer Branding & EVP Alignment
How your organization is perceived in the talent market significantly impacts attraction. This stage focuses on consistently communicating your unique Employee Value Proposition (EVP) across all touchpoints. Inputs include your defined EVP and brand guidelines. Actions involve ensuring brand messaging consistency on the career site, job boards, social media, and recruitment marketing materials. Optimizing the career site user experience (UX) and actively showcasing social proof (employee testimonials, awards) are crucial. The output is a compelling and authentic employer brand presence that attracts relevant candidates. Success can be measured by metrics like brand impression lift or application conversion rates.
3. Sourcing & Talent Mapping
With requisitions approved and the brand defined, active sourcing begins. This involves a multi-channel approach, blending inbound strategies (attracting applicants through job postings and career sites) and outbound sourcing (proactively identifying and engaging passive candidates). Effective talent pool management, utilizing CRM technology, is crucial for identifying and nurturing potential future hires. Critically, Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) principles must be embedded throughout sourcing to build representative pipelines. Outputs include a qualified pool of initial candidates. Key KPIs include the source-of-hire mix and diversity metrics within the applicant pool.
4. Candidate Engagement & Nurture
Attracting initial interest isn't enough; sustained engagement is key. This step focuses on building relationships with potential hires. Utilizing a Talent CRM enables personalized communication and automated nurture sequences, keeping candidates informed and engaged even when immediate roles are not available. Actions include providing timely responses, offering valuable content (such as company insights and team spotlights), and tailoring interactions to candidate profiles. The output is a warm pipeline of engaged candidates who view the organization favorably. Measuring response rates and nurture campaign engagement rates indicates effectiveness.
5. Assessment & Interview Design
Evaluating candidates requires the use of structured, fair, and relevant methods. This stage involves designing assessments and interviews that focus on the skills and competencies outlined in the success profile, aligning with skills-first principles. Inputs are the defined role requirements and success profile. Actions include implementing standardized skills assessments (technical or soft skills), designing structured interviews with consistent questions and evaluation rubrics, and training interviewers to mitigate unconscious bias. The output is objective, comparable data on candidate capabilities. Time-in-stage and assessment pass-through rates are key performance indicators (KPIs). These talent acquisition process steps are critical for ensuring fairness and predictive validity.
6. Selection & Offer Management
Based on assessment data and interview feedback, the selection decision is made. This involves using candidate scorecards for objective comparison against the defined success profile. Actions include conducting final interviews, completing background checks accurately, benchmarking compensation, structuring a compelling offer, and navigating the internal offer approval process efficiently. A streamlined process is vital to avoid losing top candidates at this late stage. The output is an accepted offer and a new hire. The offer acceptance rate is the primary key performance indicator (KPI) here.
7. Onboarding & 90-Day Ramp
Talent acquisition doesn't end when the offer is accepted; effective onboarding is crucial for integration and long-term retention. This stage focuses on transitioning the new hire smoothly into the organization and their role. Inputs include the offer details and new hire information. Actions involve structured pre-boarding activities, such as completing paperwork and setting up IT, assigning an onboarding buddy or mentor, establishing clear 30-60-90 day goals, providing necessary training, and actively gathering feedback on the onboarding experience. The output is a productive, integrated employee on track for success. Key KPIs include new-hire ramp-time, 90-day retention rates, and the new-hire Quality of Hire metric.
Measuring Success: Talent Acquisition Metrics to Track
| Metric | Formula / Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Time-to-Fill | Days from requisition approval to offer acceptance | Measures overall process speed and efficiency |
| Time-to-Hire | Days from posting/sourcing start to candidate start date | Measures speed from active recruitment to onboarding |
| Cost-per-Hire | Total recruitment costs ÷ number of hires | Tracks spending efficiency |
| Quality of Hire | New hire performance + retention + manager satisfaction | Assesses long-term value and success of hires |
| Source Effectiveness | % of hires or qualified candidates by channel | Identifies highest-ROI sourcing channels |
| Offer Acceptance Rate | (Offers accepted ÷ offers extended) × 100 | Indicates offer competitiveness and candidate experience |
| Candidate NPS | Net Promoter Score from candidate surveys | Measures overall satisfaction with the recruitment process |
Dashboards, potentially built using tools like Google Looker Studio or integrated within your ATS/Talent Intelligence platform, provide essential visibility for tracking these metrics and making data-driven decisions.
Complete guide on 40+ recruitment metrics:

Common Pitfalls & How to Avoid Them
Even with a defined process, organizations can stumble. Be mindful of these common pitfalls:
Underestimating Employer Branding: Treating branding as an afterthought rather than a continuous effort integrated into every stage.
Avoidance: Consistently invest in and communicate your Employer Value Proposition (EVP).
Overlooking Candidate Engagement: Focusing solely on active applicants and neglecting relationship-building with passive talent or silver medalists.
Avoidance: Implement robust Candidate Relationship Management (CRM) practices and develop effective nurturing strategies.
Neglecting Feedback and Data Loops: Failing to collect or act upon feedback from candidates and hiring managers, or ignoring performance data.
Avoidance: Build systematic feedback collection and regular metric reviews into the process.
Siloed Technology & Data: Using disparate tools that don't integrate, leading to inefficiencies and fragmented data.
Avoidance: Prioritize integrated platforms (ATS, CRM, TI) or ensure strong API connections.
Next Steps & Resources
Understanding these talent acquisition process steps provides the foundation for optimizing your hiring engine. To place this within a broader context, revisit our comprehensive talent acquisition strategy guide.
For further insights, explore related resources:
- Talent Acquisition Best Practices Checklist
- Talent Acquisition Framework Canvas
FAQ: Talent Acquisition Process Steps Explained
What are the 7 talent acquisition process steps?
The core steps are workforce planning, employer branding, sourcing, candidate engagement, assessment/interviewing, selection/offer, and onboarding.
How long should each step take?
Duration varies significantly based on role complexity, market conditions, sourcing channel effectiveness, assessment depth, and internal process efficiency; tracking time-in-stage KPIs helps identify norms and bottlenecks specific to your organization.
Which software supports each step?
Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) manage applications and workflow; Candidate Relationship Management (CRM) tools handle engagement and nurturing; Talent Intelligence platforms inform planning, sourcing, and benchmarking; Assessment tools evaluate skills; HRIS systems manage onboarding.
How do I measure quality of hire?
Quality of hire is typically measured using a combination of metrics tracked post-hire, including new hire performance ratings, achievement of 90-day goals, retention rates (e.g., at 6 months or 1 year), and hiring manager satisfaction surveys.





