The article will give an overview of Structured Hiring, its practice in a business, the core principles of the structured hiring approach, the parties involved, its impact on the hiring process, and how to conduct Structured Hiring.
Introduction
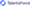
According to a CareerBuilder survey, professional recruiters responded that their decisions are wrong 75% of the time. This shows that finding a practical and structured recruitment approach will help recruiters identify the essential elements of a suitable candidate, thus saving time and money. Most importantly, sustainably hiring the right talent leads to increased recruitment ROI.
Overview of Structured Hiring
Structured Hiring is a strategic approach designed to optimize the recruitment process from start to finish. Organizations can significantly increase the likelihood of hiring top talent who will drive meaningful results by prioritizing a role's business objectives, implementing standardized evaluation methods, and making data-driven decisions.
Core principles of Structured Hiring
Structured Hiring rests on a foundation of transparent, standardized practices designed to identify and select the most qualified candidates for a given role. Key principles include:
1. Clear job definitions
Thorough job analysis forms the foundation of Structured Hiring, enabling organizations to create precise and comprehensive job descriptions by gaining insight into the specific tasks, responsibilities, and skills needed for each role.
Key steps:
- Identifying key responsibilities: Documenting the core duties and functions of the position.
- Defining required skills: Specifying the knowledge, experience, and qualifications essential for success.
- Setting performance expectations: Outlining measurable goals and objectives for the role.
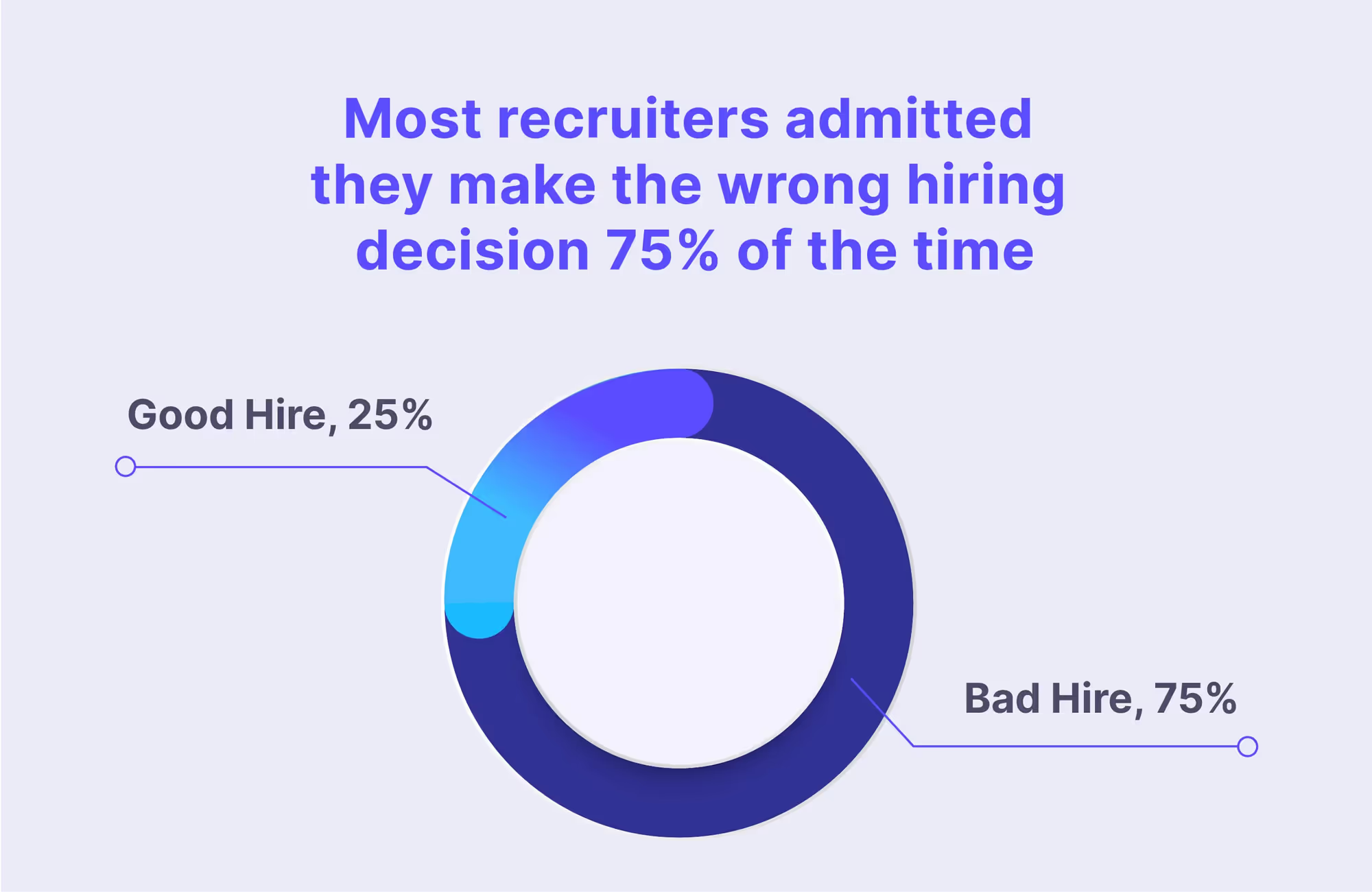
2. Standardized interview questions
Standardized interview questions are the backbone of a Structured Hiring process, ensuring consistent evaluation across all candidates. A well-defined framework should be established for each specific role, incorporating competency-based and behavioral questions to achieve this.
Competency-based questions:
These questions aim to assess a candidate's skills, knowledge, and abilities directly related to the job requirements.
- "Describe your experience with [specific software/tool] and how it has contributed to your past successes."
- "Explain your approach to [key task or responsibility outlined in the job description]."
- "Share an example of a challenging project you led and the strategies you employed to overcome obstacles."
Behavioral questions:
Examine candidates' past experiences using the STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) to uncover valuable insights.
- "Tell me about taking the initiative when resolving a conflict with a coworker. How did you approach the situation, and what was the outcome?"
- "Describe a situation where you took greater initiative and went above and beyond your assigned responsibilities. What motivated you, and what did you achieve?"
- "Share an example of a project that didn't go as planned. What did you learn from the experience, and how did you adapt?"
Scorecard and evaluation methods:
A standardized scorecard should be used to evaluate candidates' responses to maintain objectivity. The scorecard should include specific criteria aligned with the job requirements and a rating scale to assess each candidate's performance. Interviewers can then collaboratively review the scores, discuss their observations, and make informed decisions based on a comprehensive evaluation of each candidate's qualifications.
3. Team-based and Data-driven decisions
Structured Hiring involves a collaborative team approach to decision-making. By gathering input from multiple interviewers, organizations can benefit from diverse perspectives and reduce the risk of individual biases. Additionally, collecting and analyzing data from the hiring process enables continuous improvement of recruitment strategies, ensuring long-term effectiveness.
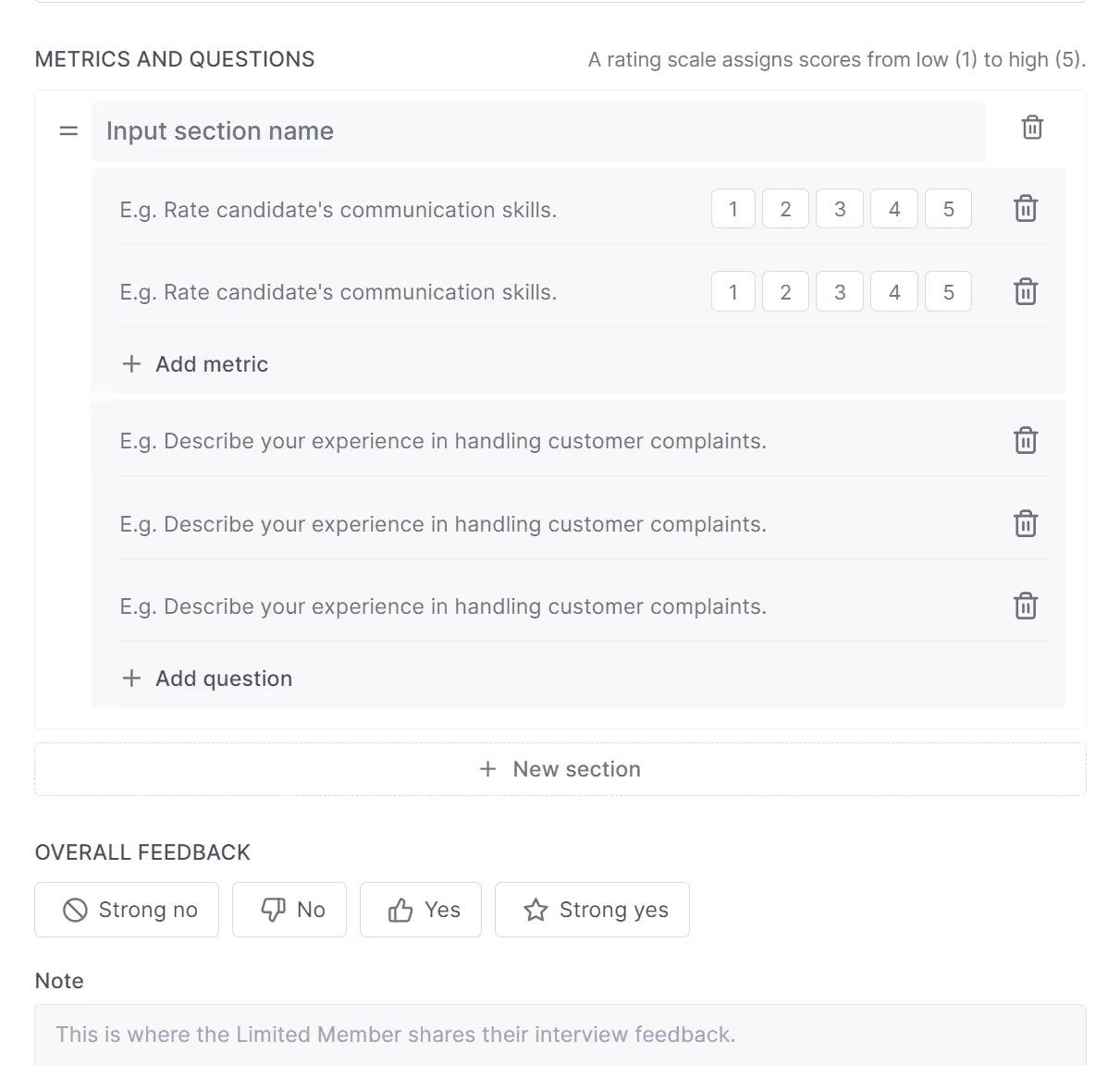
Key participants in Structured Hiring
A successful Structured Hiring process depends on the active involvement of three essential roles:
Impact of Structured Hiring
Structured Hiring enables businesses to transform the way they recruit, bringing in and selecting the very best talent with greater simplicity and confidence.
- Candidates feel confident in the process's transparency and fairness, knowing they are assessed objectively on their qualifications.
- Recruiters maintain a clear overview of the process, ensuring a smooth and efficient experience for all involved.
- Interviewers are empowered with a clear understanding of their roles and expectations, leading to more effective evaluations.
- Hiring managers confidently select candidates whose skills and experience align with the job requirements, setting them up for success from the start.
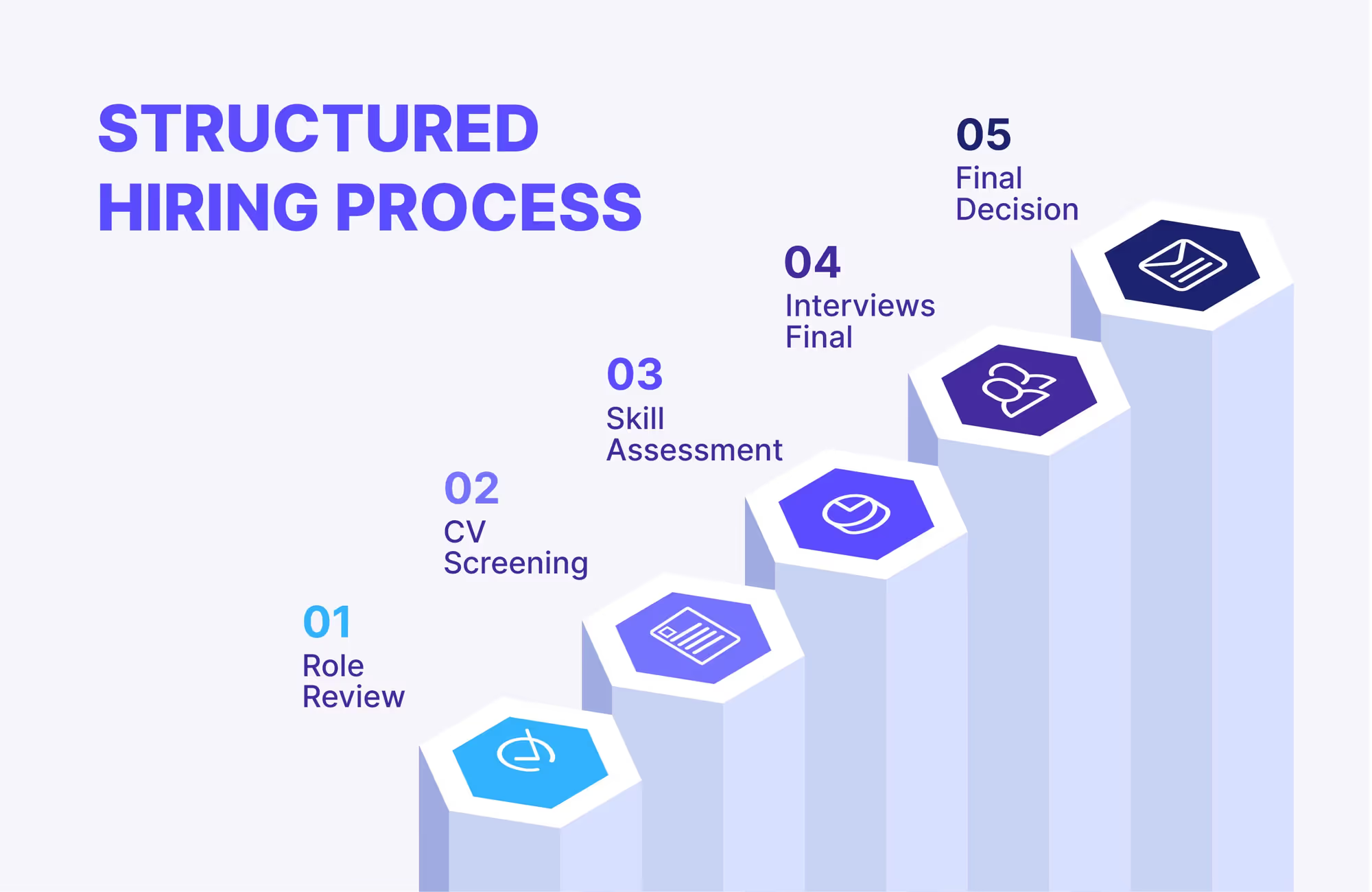
How to conduct Structured Hiring?
Role Review:
Even before the search starts, this role is completely defined. It includes the job's responsibilities, the skills needed, and even the expected experience of this ideal candidate. It's like making a blueprint for the perfect employee.
CV screening:
With this blueprint in place, recruiters will review resumes thoroughly to identify people whose qualifications best suit the role's requirements. This aids in narrowing down applicants and ensuring that only the most relevant get through.
Skill assessment:
The shortlisted candidates are then put to the test, and this part is optional based on the business and levels of the hired roles. These may consist of technical exams, practical exercises, or even case studies that test their particular competence and problem-solving skills. This can help select many individuals who have the right experience and the practical skills necessary to succeed in the role.
Final interviews:
The most promising candidates will undergo a Structured Interview process as a part of Structured Hiring. It is not just a matter of firing random questions at the candidate; they are focused on cultural fit, communication skills, and general suitability for the role. Multiple perspectives give a well-rounded view.
Final decision:
The hiring manager makes an informed decision after gathering feedback and data from the structured interview process. They choose candidates whose qualifications, skills, and personality best match the company's role and values.
Structured Hiring with Hireforce
Hireforce enables you to conduct Structured Hiring for your business. Hireforce is a new generation ATS with a simple interface that is easy to use and learn and full of tools to help recruiters set up an effective recruitment process.
Employers can create standard JDs, manage the hiring pipeline, create and save interview kits for each role, and collect feedback for candidates with customizable structures. Finally, the analytics function will help employers get a comprehensive view of the performance of the entire business recruitment process.
Features:
- Interview kits
- Collaboration within the hiring team
- Structured and team evaluation
- Analytics
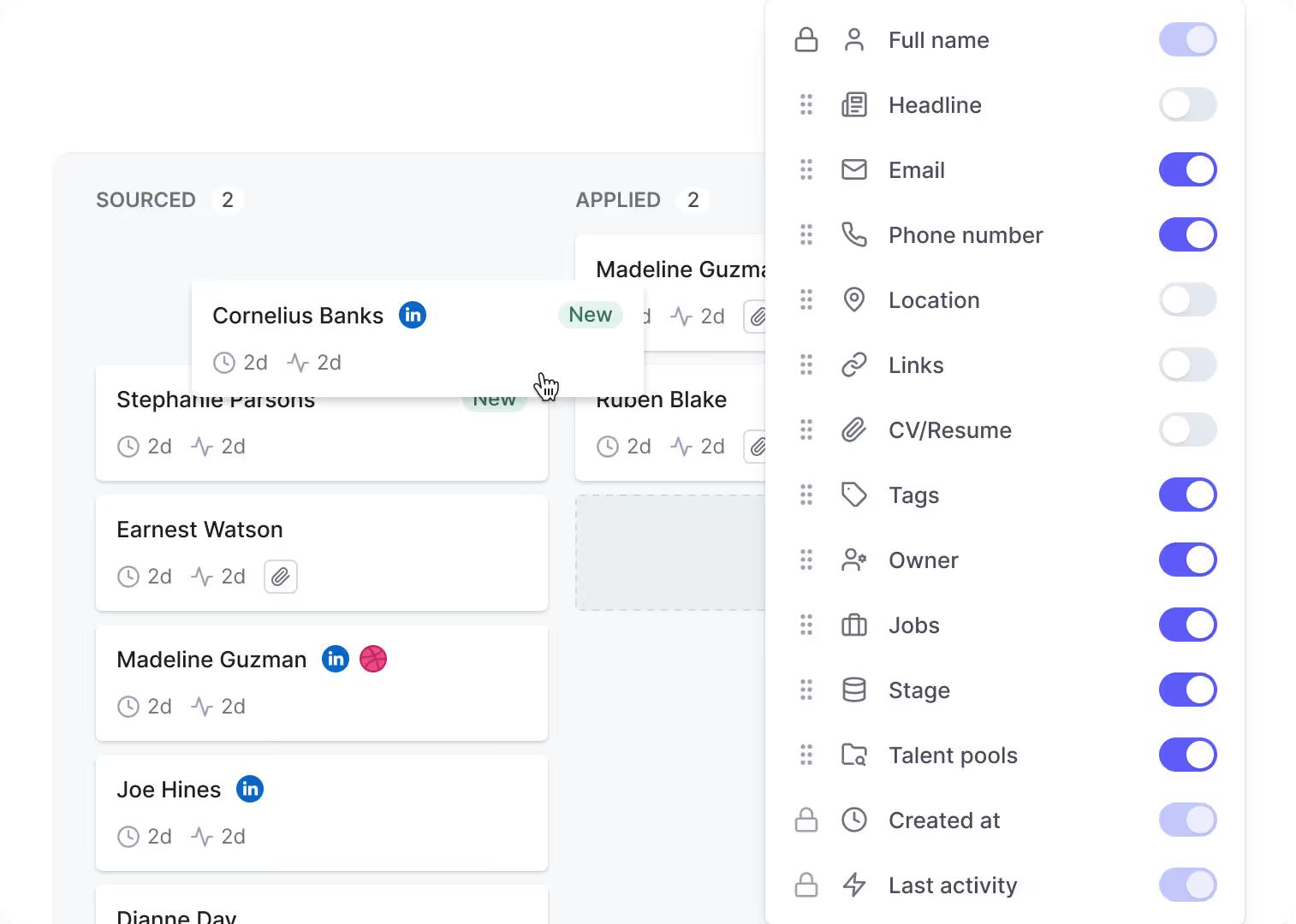
Manage the entire hiring pipeline from sourcing to job offers, and move candidates through the interview stage via drag-and-drop.
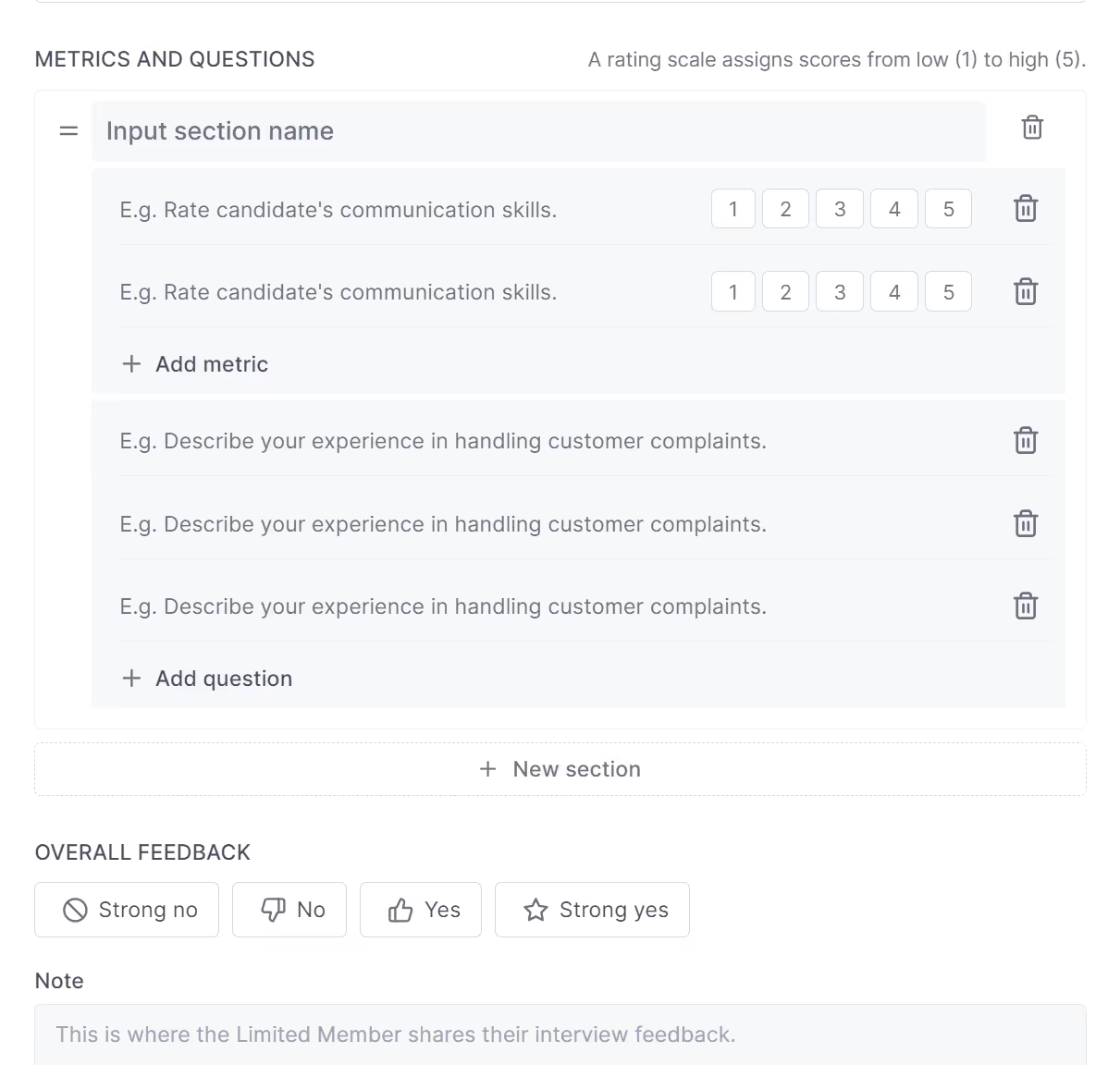
Hireforce comprehensive interview kits.